Posted by Karl Filipsson |
Papers
Two papers from NRRV were recently published in the journal Animal Conservation. The first paper presents a field study on how sedimentation affects brown trout (Salmo trutta) fry emergence in relation to freshwater pearl mussel (Margaritifera margaritifera) recruitment. The second paper presents a combined field and laboratory study on passage solutions for upstream-migrating eels (Anguilla anguilla).
Sedimentation affects emergence rate of host fish fry in unionoid mussel streams
– Martin Österling
In the abstract, the author writes:

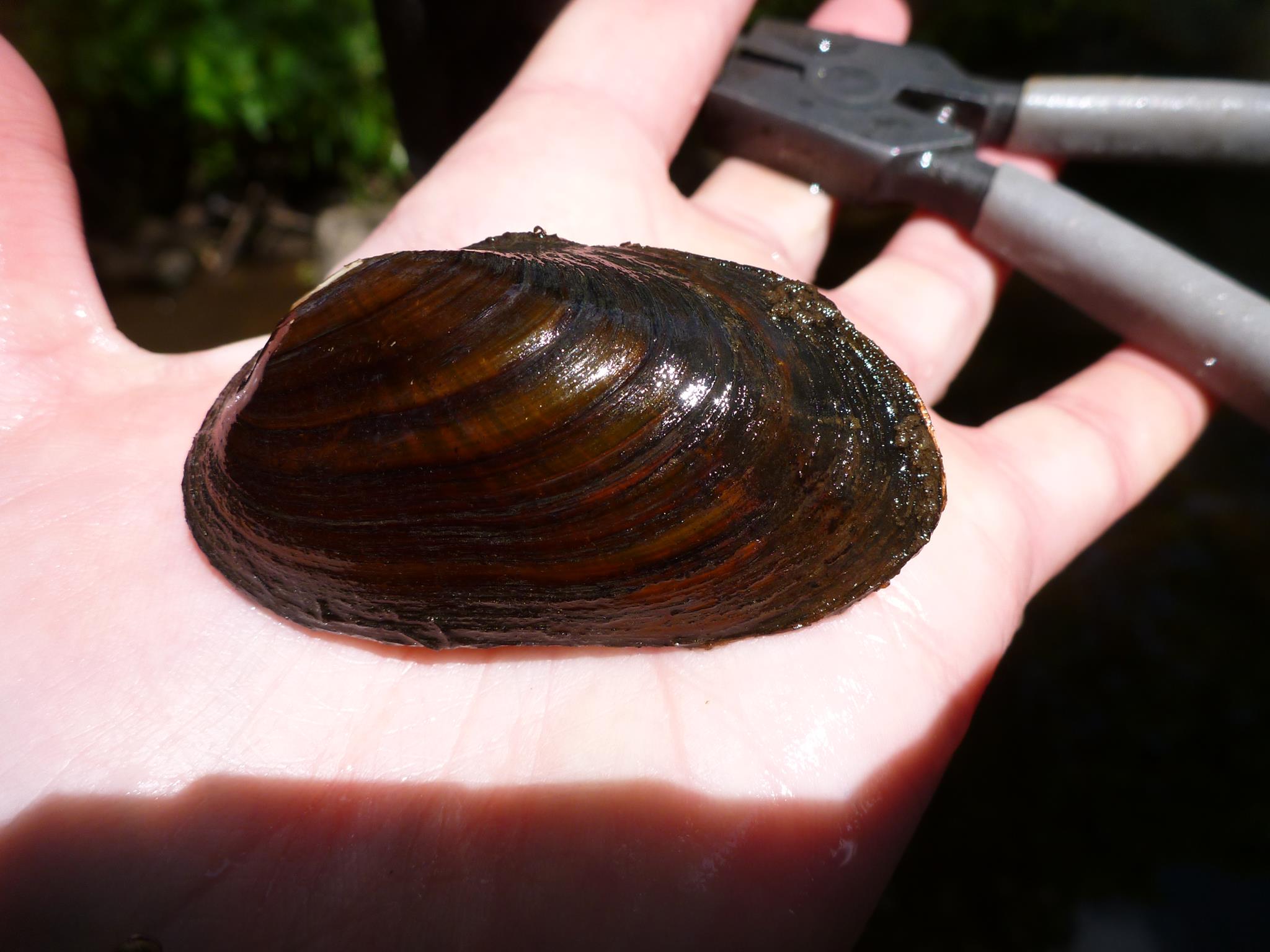
Freshwater pearl mussel, Margaritifera margaritifera
“Free-living, sympatric sedentary life stages of hosts and parasites are often adapted to similar environmental conditions. When the environment where these life stages occur is disturbed, both species can decline, causing strong negative effects on the parasitic species. For the highly threatened unionoid mussels with their larval parasitic life stage on fish, habitat degradation may simultaneously affect the conditions for the sedentary host fish eggs and the juvenile mussels in the sediment. This study provides novel information on the effect of sedimentation on the emergence rate of yolk sac fry, and its relation to mussel recruitment in two drainage basins, and is exemplified by the brown trout Salmo trutta, host fish for the threatened freshwater pearl mussel Margaritifera margaritifera. The results imply that turbidity and sedimentation can reduce the survival of trout eggs and yolk sac fry emergence rate regardless of trout strain and drainage basin. The results further suggest that low yolk sac fry emergence rates reduce the potential for mussel infestation and recruitment. The results indicate a year round negative effect of sedimentation, having strong and combined direct and indirect effects on juvenile mussel recruitment. Conservation measures that reduce anthropogenic sediment transportation into streams are a key factor for the conservation of mussels and their host fish.”
Access the paper here, or contact the author.
Climbing the ladder: an evaluation of three different anguillid eel climbing substrata and placement of upstream passage solutions at migration barriers
– Johan Watz, Anders Nilsson, Erik Degerman, Carl Tamario and Olle Calles
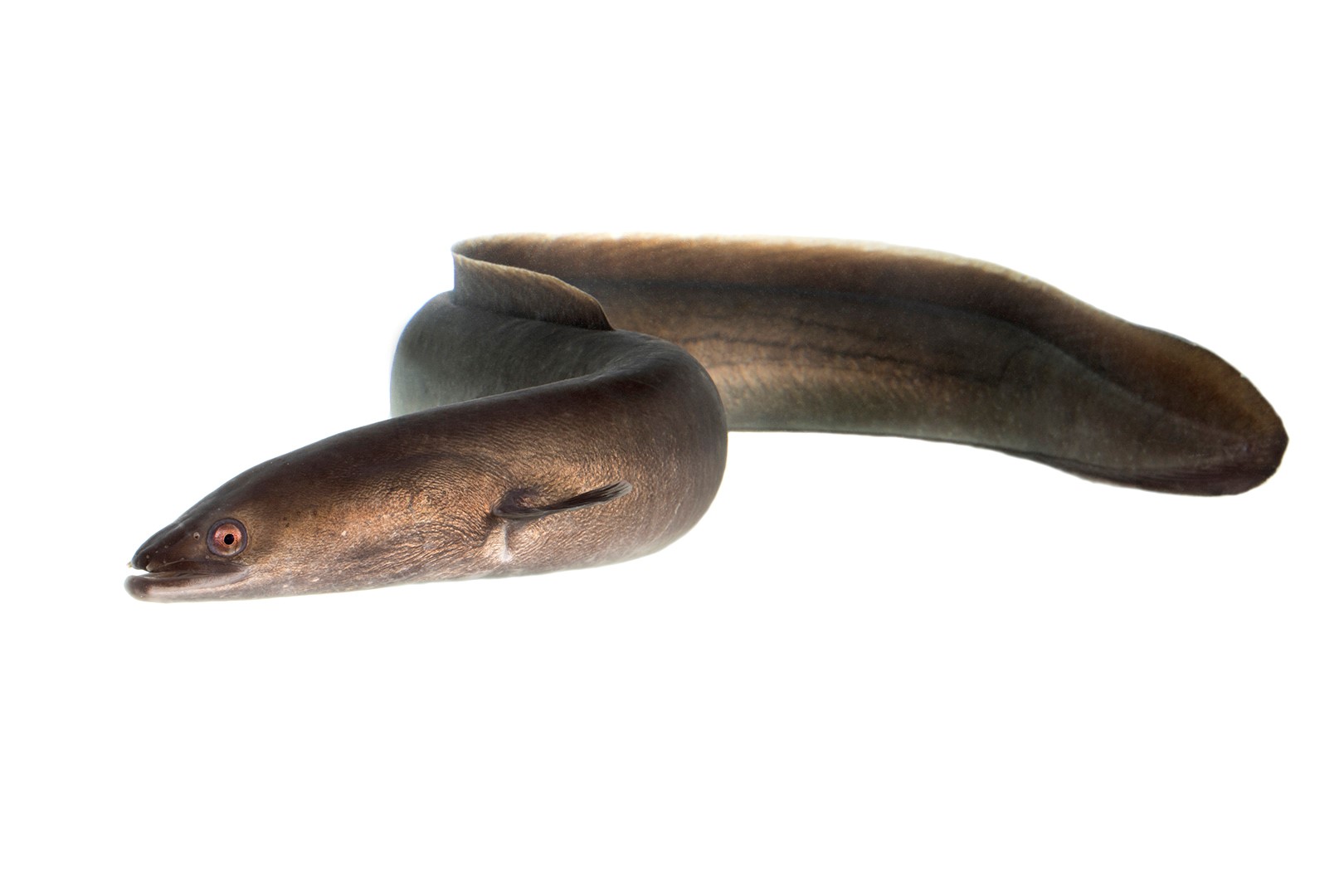

European eel, Anguilla anguilla. Photo: Jörgen Wiklund
In the abstract, the authors write:
“Conservation programmes for endangered, long-lived and migratory species often have to target multiple life stages. The bottlenecks associated with the survival of juvenile anguillid eels migrating into inland waters, the survival and growth of the freshwater life stage, as well as the recruitment and survival of silver eels, migrating back to the ocean to spawn, must be resolved. In this study, we focus on the efficiency of passage solutions for upstream-migrating juveniles. Such solutions can consist of inclined ramps lined with wetted climbing substrata. We evaluated different commonly used substrata in a controlled experiment, recorded eel behaviour at the entrance of the ramp with infrared videography and validated the experimental results at a hydropower dam, where we also investigated the effects of ramp placement on performance. In the experiment on eel substratum selection, 40% of the eels passed in lanes with studded substratum, whereas only 21 and 5% passed using open weave and bristle substrata respectively. Video analysis revealed that the studded substratum attracted more approaches and initiated climbs than the other substrata, but once a climb had been initiated, passage success rates did not differ between substrata. Eels using the studded substratum climbed 26% faster than those using the bristle substratum and almost four times as fast as those climbing in the open weave. The superior performance of the studded substratum was supported by data from the field validation. Moreover, ramps positioned by the bank with low water velocities caught the most eels, but proximity to the dam had no effect on performance. To strengthen the European eel population, more juveniles need to reach their freshwater feeding grounds. A critical step to achieve this increase is to equip upstream passage solutions with suitable substrata and to optimize ramp placement at migration obstacles.”
Access the paper here, or contact any of the authors.
 On 28 May (tomorrow), Martin Österling, Associate Professor at Karlstad University, will give a seminar titled:
On 28 May (tomorrow), Martin Österling, Associate Professor at Karlstad University, will give a seminar titled:



 Forskare i NRRV har under hösten påbörjat ett projekt inom ett för forskargruppen helt nytt ämnesområde. Det handlar om rörelsemönster hos den spanska skogssnigeln, även kallad mördarsnigel. Mördarsnigeln är en ovälkommen gäst i mångas trädgårdar, där den kan orsaka stor skada genom att äta rent i odlingar och blomsterrabatter. Det är en främmande art i Sverige, som mest troligt har kommit hit när ägg följt med plantor, jord, krukor och annan trädgårdsutrustning.
Forskare i NRRV har under hösten påbörjat ett projekt inom ett för forskargruppen helt nytt ämnesområde. Det handlar om rörelsemönster hos den spanska skogssnigeln, även kallad mördarsnigel. Mördarsnigeln är en ovälkommen gäst i mångas trädgårdar, där den kan orsaka stor skada genom att äta rent i odlingar och blomsterrabatter. Det är en främmande art i Sverige, som mest troligt har kommit hit när ägg följt med plantor, jord, krukor och annan trädgårdsutrustning.




